Many times, We will share some folder with our colleges in company and forget to remove sharing after wards... after few days, we will forget, what are all folders we shared... Even i experienced same....
I found Windows desktop command, which can list all shared folders including its path...
Type below command at command prompt...
net share
Sunday, September 19, 2010
Monday, April 12, 2010
How does DTH network work
A DTH service provider has to lease Ku-band transponders from the satellite. The encoder converts the audio, video and data signals into the digital format and the multiplexer mixes these signals. At the user end, there will be a small dish antenna and set-top boxes to decode and view numerous channels On the user's end, receiving dishes can be as small as 45 cm in diametre.
DTH is an encrypted transmission that travels to the consumer directly through a satellite. DTH transmission is received directly by the consumer at his end through the small dish antenna. A set-top box, unlike the regular cable connection decodes the encrypted transmission.
The Ku band pronounced "kay-yoo" is a portion of the electromagnetic spectrum in the range of frequencies. This symbol refers to "K-under" (in the original German, "Kurz-unten", with the same meaning)—in other words, the band directly below the K-band. In radar applications, it ranges from 12 to 18GHz according to the formal definition of radar frequency band nomenclature in IEEE Standard 521-2002.
Tuesday, March 30, 2010
High-definition television
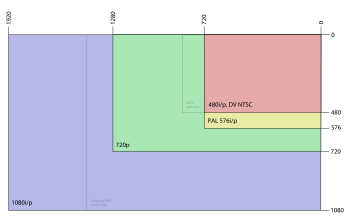
High-definition television (or HDTV, or just HD) refers to video having resolution substantially higher than traditional television systems (standard-definition TV, or SDTV, or SD). HD has one or two million pixels per frame, roughly five times that of SD
HDTV broadcast systems are identified with three major parameters:
- Frame size in pixels is defined as number of horizontal pixels × number of vertical pixels, for example 1280 × 720 or 1920 × 1080. Often the number of horizontal pixels is implied from context and is omitted.
- Scanning system is identified with the letter P for progressive scanning or I for interlaced scanning.
- Frame rate is identified as number of video frames per second. For interlaced systems an alternative form of specifying number of fields per second is often used.
While referring to HDTC Specifications, we usually 1080p, what does it mean here....
1080 horizontal lines with Progressive scanning...(Another type of well known scanning Interleaving..)
High-definition display resolutions
| Video format supported | Native resolution (W×H) | Pixels | Aspect ratio (W:H) | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actual | Advertised (Mpixel) | Image[clarification needed] | Pixel[clarification needed] | |||
| 720p 1280x720 | 1024×768 XGA | 786,432 | 0.8 | 16:9[clarification needed] | 4:3[clarification needed] | Typically a PC resolution (XGA); also a native resolution on many entry-level plasma displays with non-square pixels. |
| 1280×720 | 921,600 | 0.9 | 16:9 | 1:1 | Standard HDTV resolution and a typical PC resolution (WXGA), frequently used by video projectors; also used for 750-line video, as defined in SMPTE 296M, ATSC A/53, ITU-R BT.1543. | |
| 1366×768 WXGA | 1,049,088 | 1.0 | 683:384 (approx. 16:9) | 1:1 approx. | A typical PC resolution (WXGA); also used by many HD ready TV displays based on LCD technology. | |
| 1080p/1080i 1920×1080 | 1920×1200 | 2,073,600 | 2.1 | 16:10 | 1:1 | Standard HDTV resolution, used byFull HD and HD ready 1080p TV displays such as high-end LCD, Plasma and rear projection TVs, and a typical PC resolution (lower than WUXGA); also used for 1125-line video, as defined in SMPTE 274M, ATSC A/53, ITU-R BT.709; |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Monday, March 29, 2010
What is TAR File?
Tar (derived from tape archive and commonly referred to as "tarball") is both a file format(in the form of a type of and the name of a program used to handle such files.
Conventionally, uncompressed tar archive files have names ending in ".tar".
Unlike ZIP archives, tar files (somefile.tar) are commonly compressed as a whole rather than piecemeal. Applying a utility such as gzip, bzip2, lzip, lzma or compress to a tar file produces a compressed tar file, typically named with an extension indicating the type of compression ( e.g.: somefile.tar.gz).
A tar file is the concatenation of one or more files. Each file is preceded by a 512-byte record. The file data is written unaltered except that its length is rounded up to a multiple of 512 bytes and the extra space is zero filled. The end of an archive is marked by at least two consecutive zero-filled records. (The origin of tar's record size appears to be the 512-byte disk sectors used in the Version 7 Unix file system.)
Conventionally, uncompressed tar archive files have names ending in ".tar".
Unlike ZIP archives, tar files (somefile.tar) are commonly compressed as a whole rather than piecemeal. Applying a utility such as gzip, bzip2, lzip, lzma or compress to a tar file produces a compressed tar file, typically named with an extension indicating the type of compression ( e.g.: somefile.tar.gz).
A tar file is the concatenation of one or more files. Each file is preceded by a 512-byte record. The file data is written unaltered except that its length is rounded up to a multiple of 512 bytes and the extra space is zero filled. The end of an archive is marked by at least two consecutive zero-filled records. (The origin of tar's record size appears to be the 512-byte disk sectors used in the Version 7 Unix file system.)
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)